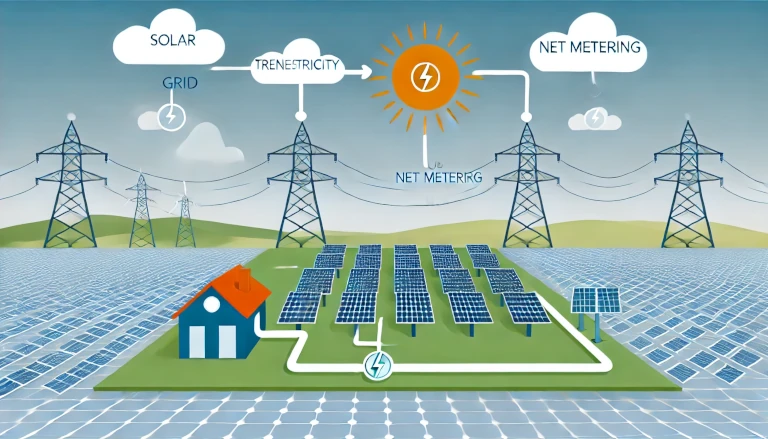
An on-grid solar system is a solar energy solution that connects directly to the public electricity grid. Also known as grid-tied or grid-connected systems, these setups generate electricity from sunlight and feed any excess power back to the grid, allowing you to offset electricity costs through net metering.
Why Choose an On-Grid Solar System? 💡
An on-grid system is ideal for anyone looking to reduce electricity bills and benefit from net metering. Net metering enables you to earn credits for the extra energy generated, which can be used to offset your future utility bills. This setup is highly suitable for homes and businesses in areas with reliable grid access and where maximizing cost savings is a priority.
How Does an On-Grid Solar System Work? 🏠
An on-grid solar system works by converting sunlight into electricity using solar panels. This electricity is converted from DC to AC by an inverter, making it usable for household appliances. If you generate more power than you use, the surplus goes back to the grid, effectively turning your utility meter backward and reducing your energy costs.
- Solar Panels 🌞: Capture sunlight and generate DC electricity.
- Inverter 🔄: Converts DC electricity into AC, compatible with the household grid.
- Net Meter ⚖️: Tracks power sent to and received from the grid, calculating energy credits through net metering.
Where Can On-Grid Solar Systems Be Used? 🏙️
On-grid solar systems are best suited for locations with dependable grid infrastructure, such as urban and suburban areas. They’re commonly used in residential properties, commercial buildings, and industrial facilities where electricity costs are high and reducing utility bills is a significant incentive.
What are the Benefits of On-Grid Solar Systems? 🌍
- Cost Savings 💰: On-grid systems significantly reduce electricity bills, and with net metering, excess energy sent to the grid can lower future costs.
- Low Maintenance 🧹: These systems are relatively easy to maintain, as there are no batteries involved.
- Environmental Impact 🌱: By using renewable energy, on-grid systems reduce carbon emissions and dependency on fossil fuels.
- Reliable Power Supply ⚡: Since the system is connected to the grid, you have a consistent power supply, even when solar production fluctuates.
How Much Does an On-Grid Solar System Cost? 💵
The cost of an on-grid solar system depends on factors like system size, location, and installation fees. While initial costs can range from a few thousand to tens of thousands of dollars, government incentives and long-term savings make it a financially appealing investment. On average, an on-grid solar system can pay for itself within 5-7 years through energy savings and net metering benefits.
Example Use Case: Residential On-Grid Solar System 🌅
A typical household installs a 5kW on-grid system. During the day, the system generates electricity, powering the home and sending excess energy to the grid. At night or during cloudy periods, the household draws electricity from the grid, and thanks to net metering, the homeowner receives credits, effectively reducing their utility bills.
Is an On-Grid Solar System Right for You? ☀️
If you have reliable access to the public electricity grid and are looking to lower your electricity bills while contributing to environmental sustainability, an on-grid solar system is a wise choice. Its cost-effectiveness, ease of maintenance, and net metering advantages make it a popular option for homeowners and businesses alike.
Discover more from Green Ecosystem - Renewable Energy, Agriculture, and Environmental Sustainability
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.